Overview of DNA Damage
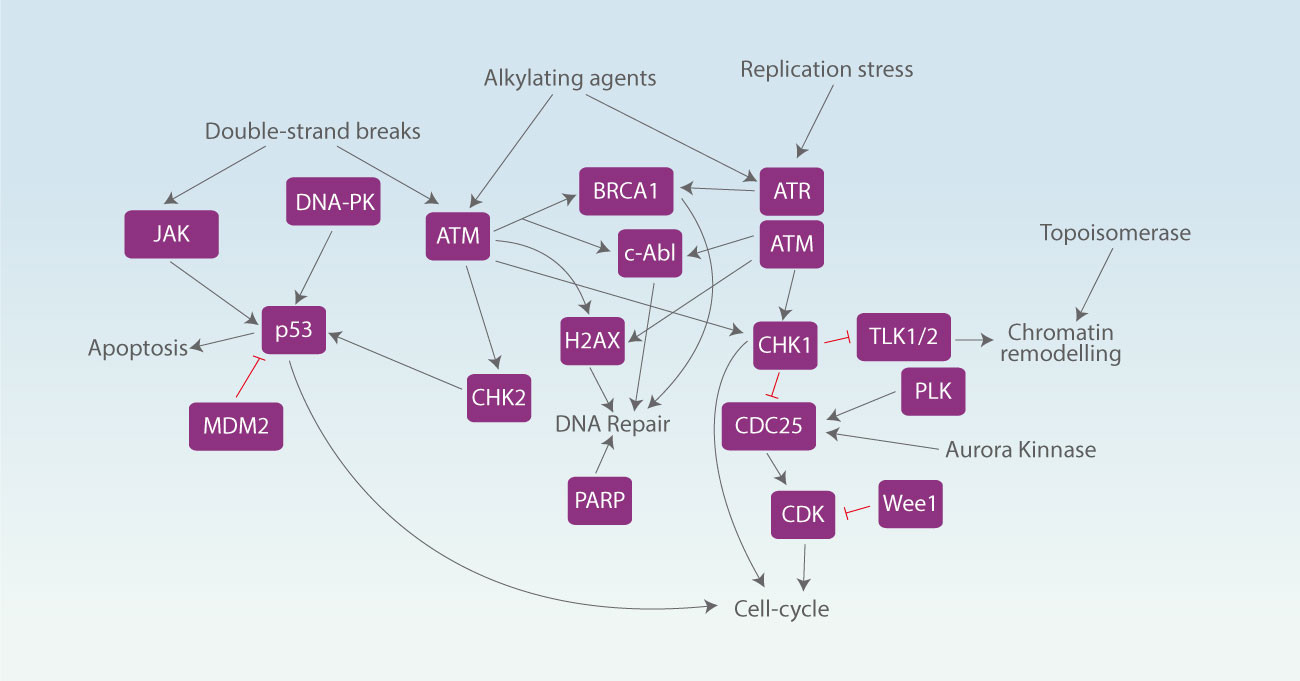
DNA damage is an alteration in the chemical structure of DNA, such as a break in a strand of DNA, a base missing from the backbone of DNA, or a chemically changed base such as 8-OHdG. Damage to DNA that occurs naturally can result from metabolic or hydrolytic processes. Metabolism releases compounds that damage DNA including reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, reactive carbonyl species, lipid peroxidation products and alkylating agents, among others, while hydrolysis cleaves chemical bonds in DNA. DNA damage response (DDR) is a series of regulatory events including DNA damage, cell-cycle arrest, regulation of DNA replication, and repair or bypass of DNA damage to ensure the maintenance of genomic stability and cell viability. Genome instability arises if cells initiate mitosis when chromosomes are only partially replicated or are damaged by a double-strand DNA break (DSB). To prevent cells with damaged DNA from entering mitosis, ATR inhibits cyclin B/Cdk1 activation by stimulating the Cdk1 inhibitory kinase Wee1 and inhibiting Cdc25C via Chk1, besides, ATM and ATR also initiate DNA repair by phosphorylating several other substrates.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
