All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
In vitro: Thiamine (50 mM), in addition to its nutritional value, induces systemic acquired resistance (SAR) in rice, tobacco, cucumber, and Arabidopsis. Thiamine-treated rice, Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana), and vegetable crop plants shows resistance to fungal, bacterial, and viral infections. Thiamine treatment induces the transient expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes in rice and other plants. In addition, Thiamine treatment potentiates stronger and more rapid PR gene expression and the up-regulation of protein kinase C activity. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced inhibition of myocyte shortening in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) effectively blunts the acetaldehyde-induced depression in ±dL/dt in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced shortening of time-to-peak shortening in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Vitamin B1 (10 μM) prevents acetaldehyde-induced elevation in both protein carbonyl formation and caspase-3 activation in adult rat ventricular myocytes. Thiamine uptake is energy- and temperature-dependent, pH-sensitive, Na+-independent, saturable at both the nanomolar (apparent Km, 30 nM) and the micromolar (apparent Km, 1.72 mM) concentration ranges in ARPE-19 cells. Uptake of Thiamine is adaptively regulated by extracellular substrate level via transcriptionally mediated mechanisms that involve both hTHTR-1 and hTHTR-2 in ARPE-19 cells, it is also regulated by an intracellular Ca2+-calmodulin-mediated pathway. Thiamine-responsive megaloblastic anemia (TRMA) fibroblasts are rescued from death with 10 nM-30 nM Thiamine (in the range of normal plasma thiamine concentrations). Normal fibroblasts exhibits saturable, high-affinity thiamine uptake (Km 400 nM-550 nM; Vmax 11 pmol/min/1×106 cells), while TRMA fibroblasts lacks detectable high-affinity uptake. At 30 nM Thiamine, the rate of uptake of Thiamine by TRMA fibroblasts is 10-fold less than that of wild-type, which explains the increased apoptosis of TRMA fibroblasts.
In vivo: Thiamine deficiency results in amyloid precursor protein immunoreactivity accumulated in swollen neurites within, or around lesions in rats, or in abnormal clusters in mice.
| Cell Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Cell lines | HL-60 cells |
| Preparation method | HL-60 cells were pre-treated with 0.25 μg/ml of either cycloheximide or tetrathylammonium, a big potassium channel (BK) blocker, for 2 hours and then cultured for 12 hours with or without thiamine (100 μM) and stained with Giemsa. |
| Concentrations | 100 μM |
| Incubation time | 12 h |
| Animal Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Animal models | |
| Formulation | |
| Dosages | |
| Administration | |
| Molecular Weight | 337.27 |
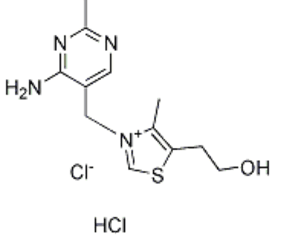
| Formula | C12H17N4OS.HCl |
| CAS Number | 67-03-8 |
| Solubility (25°C) | Water 90 mg/mL |
| Storage | 4°C, protect from light, dry, sealed |
| Related Vitamin Products |
|---|
| 1alpha-Hydroxy VD4
1alpha-Hydroxy VD4 , a 1alpha(OH)D derivative, can effectively induce the differentiation of monoblastic leukaemia U937, P39/TSU and P31/FUJ cells. |
| TEI-9647
TEI-9647 is a Vitamin D3 Lactone analogue, and it is a potent and specific vitamin D receptor (VDR) antagonist. TEI-9647 blocks both 1α,25(OH)2D3-mediated HL-60 cell differentiation and also activation of the luciferase reporter in COS-7 cells that has been transfected with the cDNA containing the DRE of the rat 25(OH)D3-24-hydroxylase gene and cDNA of the human vitamin D nuclear receptor. |
| Menaquinone-7
Menaquinone-7 (Vitamin K2-7) belongs to a class of K2-vitamin homologs (orally active), it is originally discovered as the anti-hemorrhagic factors. Menaquinone-7 (Vitamin K2, MK-7) inhibits osteoclast bone resorption in vitro and stimulates bone formation in femoral tissue of aged female rats. |
| Liarozole
Liarozole (R75251) is an imidazole derivative and orally active retinoic acid (RA) metabolism-blocking agent (RAMBA). Liarozole inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP26)-dependent 4-hydroxylation of retinoic acid (IC50=7 μM). |
| VDR agonist 2
VDR agonist 2 is a VDR (vitamin D receptor) agonist that can effectively inhibit TGF-β1-induced activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSC). |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
