All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
For this product's availability, delivery time and price, please email [email protected] directly or click the "Inquiry Now" button below.
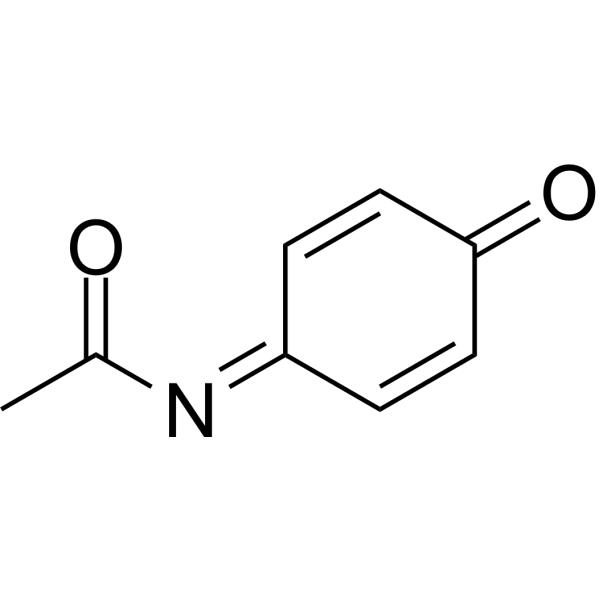
NAPQI is the toxic metabolite of Acetaminophen. NAPQI is also an inhibitor of enzymes in the vitamin K cycle. NAPQI is rapidly detoxified by glutathione (GSH), but in situations of GSH deficiency, excess NAPQI reacts with cysteine residues in proteins, causing cell death and toxicity in the liver.
| Molecular Weight | 149.15 |
| Formula | C8H7NO2 |
| CAS Number | 50700-49-7 |
| Form | Solid |
| Storage | -80°C, protect from light, sealed |
[4] Erik S Fisher, et al. Adv Pharmacol. Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity
| Related Metabolite/Endogenous Metabolite Products |
|---|
| Gentisuric Acid
Gentisuric Acid is a metabolite of Aspirin, it is a substrate of α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM). Gentisuric acid prevents DNA-damage by Mitomycin C. |
| 5α-Dihydroprogesterone
5α-Dihydroprogesterone (5a-Pregnane-3,20-dione) is the endogenous progesterone metabolite. 5α-Dihydroprogesterone (5a-Pregnane-3,20-dione) decreases cell-substrate attachment, adhesion plaques, vinculin expression, and polymerizes F-actin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. |
| Adenosine 2',3'-cyclic phosphate sodium
Adenosine 2',3'-cyclic phosphate sodium serves as an extracellular source of adenosine. The release of extracellular 2′,3′-cAMP occurs in response to injury. 2′,3′-cAMP may be used to study the distribution and specificity of its degrading enzymes in the context of unique biological activities. 2′,3′-cAMP may also be used to study apoptosis induced at the level of mitochondrial permeability transition pores. 2′,3′-cAMP is converted into 2′-AMP and 3′-AMP which inhibit proliferation of preglomerular vascular smooth muscle cells and glomerular mesangial cells via A2B receptors. |
| 6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel
6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel is a primary metabolite of Paclitaxel. 6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel (6-Hydroxytaxol) retains a time-dependent effect on organic anion-transporting polypeptides 1B1/SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) with similar inhibition potency to Paclitaxel, whereas it no longer showed time-dependent inhibition of OATP1B3. |
| Casein (from bovine milk)
Casein is a phosphorus-containing complex protein with α-casein and β-casein as its main components. Casein is an orally active phosphoprotein that can be separated into various electrophoretic components, such as α2-Casein, κ-Casein, β-casein, and γ-casein. Casein can be used in biochemical research, to formulate biological culture media, and as a thickener, emulsifier and stabiliser. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
