All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
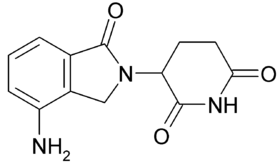
Lenalidomide (Revlimid) is a derivative of thalidomide. Lenalidomide has tumoricidal and immunomodulatory activity against multiple myeloma. Lenalidomide has also shown efficacy in the class of hematological disorders known as myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). Lenalidomide maintenance therapy, initiated at day 100 after hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation, was associated with more toxicity and second cancers. Lenalidomide has significantly improved overall survival in myeloma (which generally carries a poor prognosis), although toxicity remains an issue for users.

Blood. 2021 Dec 23;138(25):2655-2669.
Targeting intracellular WT1 in AML with a novel RMF-peptide-MHC specific T-cell bispecific antibody
Lenalidomide purchased from AbMole

BMC Biol. 2021 May 20;19(1):108.
Very long intergenic non-coding (vlinc) RNAs directly regulate multiple genes in cis and trans
Lenalidomide purchased from AbMole

Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Sep;578-87.
Resveratrol attenuates hypoxia-induced neurotoxicity through inhibiting microglial activation.
Lenalidomide purchased from AbMole
| Cell Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Cell lines | HL60, MOLM13 and NB4 cells |
| Preparation method | Spectrophotometric quantification of cell proliferation was assayed by the water soluble tetrazolium salt-1 (WST-1) (AbMole, M28552) based colorimetric assay. This tetrazolium salt is reduced extracellularly to formazan dye by enzymes of the plasma membrane oxidoreductase. The primary reductant is NADH derived from the TCA of the mitochondria. Hence, WST-1 is converted by metabolically active cells and was employed to measure cell proliferation. The cell lines HL60, MOLM13 and NB4 were plated in triplicate (20×10^3 cells/well) in a 96-well microplate and treated with either LND (1, 5, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 500 µM) . |
| Concentrations | 1, 5, 20, 50, 100, 200, and 500 µM |
| Incubation time | 48 h |
| Animal Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Animal models | NOD/scid/gamma (NSG) mice |
| Formulation | 10% DMSO, 70% PEG300 |
| Dosages | 50 mg/kg daily |
| Administration | i.p. |
| Molecular Weight | 259.26 |
| Formula | C13H13N3O3 |
| CAS Number | 191732-72-6 |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO 34 mg/mL |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
| Related TNF Receptor Products |
|---|
| Ozekibart
Ozekibart is an anti-TNFRSF10B monoclonal antibody. |
| TAPI-0
TAPI-0 is a TACE (TNF-α converting enzyme; ADAM17) inhibitor with an IC50 of 100 nM. |
| Semapimod tetrahydrochloride
Semapimod tetrahydrochloride (CNI-1493), an inhibitor of proinflammatory cytokine production, can inhibit TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. |
| BMS-566394
BMS-566394 is a potent, exceptionally selective inhibitor of TNF-α converting enzyme (TACE). |
| APVO603
APVO603 is a dual agonist bispecific antibody employing a novel mechanism of action to simultaneously target 4-1BB (CD137) and OX40 (CD134), both members of the TNF-receptor family. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
