All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
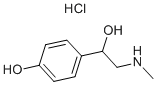
Synephrine hydrochloride (Oxedrine, p-Synephrine) is a sympathomimetic α-adrenergic receptor (AR, α-adrenoceptor) agonist. Synephrine is ~40,000-fold less potent than norepinephrine with respect to binding to β-1 and β-2 adrenoreceptors. Synephrine is ~1000-fold less active than norepinephrine in binding to rat aorta α-1 and rabbit saphenous vein α-2 adrenoreceptors. Acute intravenous administration of Synephrine reduces portal pressure and increases arteial pressure in portal vein stenosed rats in a dose dependent manner. Synephrine has been administered clinically to shock patients with effective pressor effects. In healthy human volunteers and anesthetized dogs, acute infusion of Synephrine induces both systemic pressor and positive inotropic effects, suggesting activation of both vascular α-adrenoceptors and myocardial β-adrenoceptors. Whereas repeated gavage administration of Synephrine into portal hypertensive and cirrhotic rats results in predominant activation of vascular α-adrenoceptors. Synephrine significantly ameliorates the portal hypertension and systemic as well as splanchnic hyperemic state in portal hypertensive rats induced by either partial portal vein ligation (PVL) or bile duct ligation (BDL) through splanchnic vasoconstriction, and exerts beneficial hemodynamic effects in the two models. Synephrine treatment potently leads to constriction of isolated rat aorta in a dose-dependent manner specifically via adrenergic and serotonergic (5-HT1D and 5-HT2A) receptors. Synephrine is a partial agonist of α(1A)-AR subtype, giving a maximal response at 100 μM that is equal to 55.3 % of the L-phenylephrine maximum. Similar to beta-phenethylamine, Synephrine may act as an antagonist rather than an agonist of the pre-synaptic α(2A)- and α(2C)-AR subtypes present in nerve terminals. Synephrine can stimulate glucose consumption (Glut4-dependent glucose uptake) by stimulating AMPK activity in L6 skeletal muscle cells, independent of insulin-stimulated PI3 kinase-Akt activity.
| Cell Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Cell lines | |
| Preparation method | |
| Concentrations | |
| Incubation time | |
| Animal Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Animal models | Male Sprague-Dawley rats with portal hypertension (with or without cirrhosis) induced by bile duct ligation or partial portal vein ligation |
| Formulation | Dissolved in 0.1 N HCl |
| Dosages | ~1 mg/kg per 12 hours |
| Administration | Oral gavage |
| Molecular Weight | 203.67 |
| Formula | C9H13NO2.HCl |
| CAS Number | 5985-28-4 |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
[2] No authors listed. Bitter Orange
[4] D K Song, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of p-synephrine in mouse models of immobility tests
[5] K E Ibrahim, et al. The mammalian metabolism of R-(-)-m-synephrine
| Related Adrenergic Receptor Products |
|---|
| Indoramin
Indoramin is a selective α1A-adrenoceptor antagonist. |
| Ro 363 hydrochloride
Ro 363 hydrochloride is a potent and highly selective β1-adrenoceptor agonist. Ro 363 hydrochloride is also an effective inotropic stimulant. Ro 363 hydrochloride is a cardiovascular modulator that reduces diastolic blood pressure and pronounces increases in myocardial contractility. |
| Phentolamine
Phentolamine is a potent, selective and orally active α1 adrenergic and α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist. |
| Dipivefrin
Dipivefrin is a potent adrenergic agonist. |
| HOKU-81
HOKU-81 (4-Hydroxytulobuterol) is one of the metabolites of Tulobuterol. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
