All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
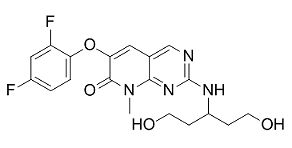
Pamapimod is a novel p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, inhibited p38alpha and p38beta enzymatic activity, with IC50 values of 0.014 +/- 0.002 and 0.48 +/- 0.04 microM, respectively. Pamapimod also inhibited lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α production by monocytes, interleukin (IL)-1β production in human whole blood, and spontaneous TNFα production by synovial explants from RA patients. LPS- and TNFα-stimulated production of TNFα and IL-6 in rodents also was inhibited by pamapimod.
In vivo: In murine collagen-induced arthritis, pamapimod reduced clinical signs of inflammation and bone loss at 50 mg/kg or greater. In a rat model of hyperalgesia, pamapimod increased tolerance to pressure in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting an important role of p38 in pain associated with inflammation.
| Cell Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Cell lines | Human Monocytic Cell Line, THP-1 |
| Preparation method | THP-1 cells, growing in log phase, were collected by centrifugation and resuspended in RPMI 1640 containing 5.5×10-5 M 2-mercaptoethanol and 10% fetal bovine serum to a final cell concentration of 2.5×106 cells/ml. Dilutions of pamapimod were predispensed in 25 μl aliquots (before addition of cells) into round-bottom 96-well plates. The starting concentration was 100 μM in 5% dimethyl sulfoxide, and six half-log serial dilutions were made. After the addition of 200 μl of cell suspension and 25 μl of 5 μg/ml LPS in medium, the final dimethyl sulfoxide concentration was 0.5%. Compounds were diluted an additional 10-fold, and the final LPS concentration was 500 ng/ml. The cell suspensions and compound dilutions were combined and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere, before the addition of LPS (or medium for non-LPS control samples). After the addition of LPS, plates were incubated for 2 h, followed by centrifugation to pellet cells. Cell supernatants were stored at 4°C until analysis for TNF-α content. TNF-α levels were determined by ELISA. Cytokine concentrations were determined. |
| Concentrations | 15 μM |
| Incubation time | 150 min |
| Animal Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Animal models | BALB/c mice |
| Formulation | 0.9% NaCl, 0.5% sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 0.4% polysorbate 80, 0.9% benzyl alcohol, and 97.3% distilled water. |
| Dosages | 25, 50, 100, 150 mg/kg |
| Administration | oral administration |
| Molecular Weight | 406.38 |
| Formula | C19H20F2N4O4 |
| CAS Number | 449811-01-2 |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO 80 mg/mL Ethanol 20 mg/mL |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
| Related p38 MAPK Products |
|---|
| SSK1
SSK1 is a senescence-specific killing compound and is a precursor for β-galactosidase, which can reduce the inflammatory response. SSK1 can activate the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and MKK3/MKK6 in senescent cells, promote mitochondrial DNA damage and selectively killed senescent cells. |
| p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor III
p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor III is a p38 MAPK inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.9 μM. p38 MAP Kinase Inhibitor III also inhibits IL-1β and TNF-α release with IC50 values of 0.37 μM and 0.044 μM, respectively. |
| (R)-STU104
(R)-STU104 is a potent and orally active TAK1-MKK3 interaction inhibitor with IC50s of 0.58 μM and 4.0 μM for TNF-α and MKK3 phosphorylation. |
| SB 706504
SB 706504 is a potent p38 MAPK inhibitor that inhibits Lipopolysaccharides-stimulated inflammatory gene expression in macrophages in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). |
| RWJ-67657
RWJ-67657 (JNJ 3026582) is an orally active and selective p38α and p38β MAPK inhibitor with IC50s of 1 and 11 μM, respectively. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
