All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
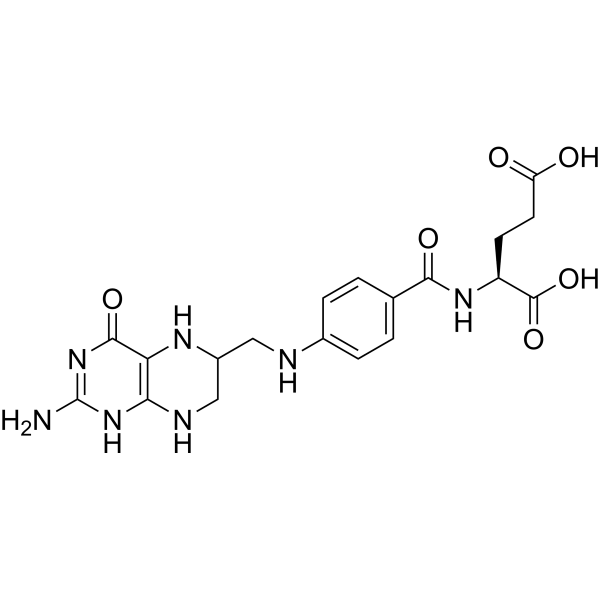
Tetrahydrofolic acid (L-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydrofolic acid) is the biologically active vitamin B9 folate derivative. Tetrahydrofolic acid is a donor of one-carbon groups for amino acids, nucleic acids, and lipids. Tetrahydrofolic acid serves as an acceptor of free formaldehyde, producing 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate-Tetrahydrofolic acid.
*The compound is unstable in solutions, freshly prepared is recommended
| Molecular Weight | 445.43 |
| Formula | C19H23N7O6 |
| CAS Number | 135-16-0 |
| Form | Solid |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO 20.83 mg/mL (ultrasonic) |
| Storage | -20°C, protect from light, sealed |
| Related Metabolite/Endogenous Metabolite Products |
|---|
| 6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel
6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel is a primary metabolite of Paclitaxel. 6α-Hydroxy Paclitaxel (6-Hydroxytaxol) retains a time-dependent effect on organic anion-transporting polypeptides 1B1/SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) with similar inhibition potency to Paclitaxel, whereas it no longer showed time-dependent inhibition of OATP1B3. |
| Casein (from bovine milk)
Casein is a phosphorus-containing complex protein with α-casein and β-casein as its main components. Casein is an orally active phosphoprotein that can be separated into various electrophoretic components, such as α2-Casein, κ-Casein, β-casein, and γ-casein. Casein can be used in biochemical research, to formulate biological culture media, and as a thickener, emulsifier and stabiliser. |
| Palmitic acid-13C16
Palmitic acid-13C16 is the 13C-labeled Palmitic acid. Palmitic acid is a long-chain saturated fatty acid commonly found in both animals and plants. |
| Methionine sulfoximine
Methionine sulfoximine (2-Amino-4-(S-methylsulfonimidoyl)butanoic acid) is an irreversible inhibitor of glutamine synthetase. Methionine sulfoximine is able to affect the metabolism of glutamate and glutamine. |
| L-Glutamine-15N2
L-Glutamine-15N2 is the 15N-labeled L-Glutamine. L-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid present abundantly throughout the body and involved in many metabolic processes. L-Glutamine provides a source of carbons for oxidation in some cells. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
