All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
In vitro: Hydroxyfasudil prevents the downregulation of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) under hypoxic conditions. In a concentration-dependent manner, hydroxyfasudil increases eNOS mRNA and protein expression, resulting in a 1.9- and 1.6-fold increase, respectively, at 10 μmol/L (P<0.05 for both). This correlates with a 1.5- and 2.3-fold increase in eNOS activity and NO production, respectively (P<0.05 for both). Hydroxyfasudil also inhibits various chemoattractant-induced migration of neutrophils. Hydroxyfasudil potently inhibits Rho-kinase (IC50, 0.9 ± 1.8 μM), while its inhibitory effect is markedly (at least 50 ± 100 times) less for myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) or protein kinase C (PKC).
In vivo: Intracoronary administration of hydroxyfasudil(HF) causes a significant coronary vasodilation of both small arteries and arterioles in a dose-dependent manner under control conditions with a resultant increase in CBF(coronary blood flow). Intracoronary hydroxyfasudil does not significantly alter mean aortic pressure or heart rate. Pretreatment with hydroxyfasudil markedly reduces the I/R-induced myocardial infarct size, and this beneficial effect of hydroxyfasudil is significantly attenuated by L-NMMA. NO may be involved in those cardiovascular protective effects of hydroxyfasudil. Hydroxyfasudil may also be effective for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. HF protects the myocardium subjected to pacing-induced ischaemia through the increase in the regional myocardial blood flow.
| Cell Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Cell lines | Human vascular endothelial cells |
| Preparation method | Human vascular endothelial cells are treated with increasing concentrations of hydroxyfasudil (0.1 to 100 μmol/L) and eNOS expression and activity are measured. |
| Concentrations | 0.1 to 100 μmol/L |
| Incubation time | 18 h |
| Animal Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Animal models | Mongrel dogs |
| Formulation | Physiologic saline |
| Dosages | 10, 30, and 100 μg/kg |
| Administration | IC(Intracoronary administration) |
| Molecular Weight | 343.83 |
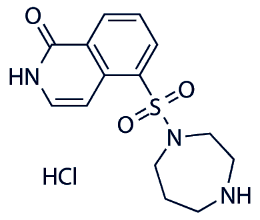
| Formula | C14H17N3O3S·HCl |
| CAS Number | 155558-32-0 |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO: ≥ 30 mg/mL |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
| Related ROCK Products |
|---|
| OXA-06 hydrochloride
OXA-06 hydrochloride is an ATP-competitive ROCK inhibitor that blocks anchorage-dependent growth and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. |
| Y-33075 hydrochloride
Y-33075 hydrochloride (Y-39983) is a selective ROCK inhibitor derived from Y-27632, and is more potent than Y-27632, with an IC50 of 3.6 nM. |
| SR-3677 dihydrochloride
SR-3677 dihydrochloride is a potent and selective ROCK-I and ROCK-II inhibitor with an IC50 values of 56 nM and 3 nM. |
| Akt/ROCK-IN-1
Akt/ROCK-IN-1 (B12) is a dual inhibitor for Akt and ROCK, with the IC50s of 0.023 nM and 1.47 nM, respectively. |
| Scaff10-8
Scaff10-8, bound to RhoA, inhibits the AKAP-Lbc-mediated RhoA activation. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
