All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
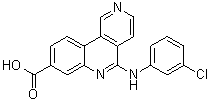
CX-4945 (Silmitasertib) is the first orally available small molecule inhibitor of protein CK2 in clinical trials for cancer. CX-4945 (Silmitasertib) selectively binds to and inhibits the enzyme casein kinase II (CK2). Protein kinase CK2 (CK2) is involved in a variety of roles essential to the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. CK2 promotes signaling in the Akt pathway and CX-4945 suppresses the phosphorylation of Akt as well as other key downstream mediators of the pathway such as p21. CX-4945 has been reported to show broad spectrum anti-proliferative activity in multiple cancer cell lines. CX-4945 induced apoptosis and caused cell cycle arrest in cancer cells in vitro. CX-4945 exhibited a dose-dependent antitumor activity in a xenograft model of PC3 prostate cancer model and was well tolerated. In vivo time-dependent reduction in the phosphorylation of the biomarker p21 at T145 was observed by immunohistochemistry.

Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 14;7(1):17569.
CK2 modulates adipocyte insulinsignaling and is up-regulated in human obesity
Silmitasertib (CX-4945) purchased from AbMole

UNIVERSITA’ DEGLI STUDI DI PADOVA. 2017.
UNDERSTANDING THE MECHANISMS OF ADIPOSE TISSUE EXPANSION IN MULTIPLE SYMMETRIC LIPOMATOSIS AND OBESITY
Silmitasertib (CX-4945) purchased from AbMole

Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1853(7):1693-701.
Protein kinase CK2 potentiates translation efficiency by phosphorylating eIF3j at Ser127.
Silmitasertib (CX-4945) purchased from AbMole

Biomed Res Int. 2015;601543.
Phosphorylation, Signaling, and Cancer: Targets and Targeting.
Silmitasertib (CX-4945) purchased from AbMole

Growth Factors. 2015 Sep 04;259-266.
Effects of CK2 inhibition in cultured fibroblasts from Type 1 Diabetic patients with or without nephropathy.
Silmitasertib (CX-4945) purchased from AbMole
| Cell Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Cell lines | BT-474 (breast) or BxPC-3 (pancreatic) cancer or HUVEC cells |
| Preparation method | A 5 mmol/L stock solution in dimethyl sulfoxide was prepared and stored at - 70 ℃. The drug was diluted directly into growth media immediately prior to use.Various cell lines were seeded at a density of 3,000 cells per well 24 hours prior to treatment, in appropriate media, and then treated with indicated concentrations of CX-4945. Suspensions cells were seeded and treated on the same day.Following 4 days of incubation, Alamar Blue (20 mL, 10% of volume per well) was added and the cells were further incubated at 37 C for 4–5 hours. Fluorescence with excitation wavelength at 530–560 nm and emission wavelength at 590 nm was measured. |
| Concentrations | 0, 0.1, 1.0, 5.0, 10 µM |
| Incubation time | 24 h |
| Animal Experiment | |
|---|---|
| Animal models | Female immunocompromised mice CrTac:Ncr-Foxn1nu (5–7 weeks old) BT474 or BxPC-3 cells Xenografts |
| Formulation | Solubilized in DMSO and diluted with PBS containing 10% dimethylacetamide (Sigma-Aldrich) and 6% Solutol (Sigma-Aldrich). |
| Dosages | twice daily at 25 or 75 mg/kg for 31 and 35 consecutive days |
| Administration | oral gavage |
| Molecular Weight | 349.77 |
| Formula | C19H12ClN3O2 |
| CAS Number | 1009820-21-6 |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO ≥ 46 mg/mL |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
[3] Ferguson et al. FEBS Lett. Structural basis of CX-4945 binding to human protein kinase CK2.
| Related Casein Kinase Products |
|---|
| SJ3149
SJ3149 is a selective and potent degrader of CK1α protein in vitro and in vivo. |
| CK1α degrader-1
CK1α degrader-1 is an orally active CK1α degrader with a DC50 of 0.105 μM. |
| ON 108600
ON 108600 is an inhibitor of CK2 (Casein Kinase2)/TNIK/DYRK1 with IC50 values of 0.016 μm/0.007 μM, 0.028 μM, 0.05 μM/0.005 μM, and 0.005 μM for DYRK1A/DYRKB, DYRK2, CK2α1/CK2α2, and TNIK, respectively. 0.005 μM. It has anti-tumor activity. |
| (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride
(R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride is a potent inhibitor of casein kinase 1 (CK1), CDK1/cyclin B, and CDK5/p25, with IC50s of 14 nM, 220 nM, and 80 nM, respectively.(R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride prevented the production of CK1-dependent amyloid-β in cellular models. In addition, (R)-DRF053 dihydrochloride prevented the production of CK1-dependent amyloid-β in cell models. |
| Casein kinase 1δ-IN-5
Casein kinase 1δ-IN-5 is a potent and selective protein kinase CK-1δ inhibitor with an IC50 of 47 nM, which has neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties in vitro. It has neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties in vitro. It can be used in studies related to neurodegenerative diseases. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
