All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption.
In vitro: Phenformin stimulates the phosphorylation and activation of AMPKalpha1 and AMPKalpha2 without altering LKB1 activity. Phenformin increases AMPK activity and phosphorylation in the isolated heart, the increase in AMPK activity is always preceded by and correlated with increased cytosolic [AMP]. Phenformin is a 50-fold more potent inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I than metformin. Phenformin robustly induces apoptosis in LKB1 deficient NSCLC cell lines. Phenformin at 2 mM similarly induces AMPK signaling as shown by increased P-AMPK and P-Raptor levels. Phenformin induces higher levels of cellular stress, triggering induction of P-Ser51 eIF2α and its downstream target CHOP, and markers of apoptosis at later times. Phenformin and AICAR increases AMPK activity in H441 cells in a dose-dependent fashion, stimulating the kinase maximally at 5-10 mm and 2 mm, respectively. Phenformin significantly decreases basal ion transport (measured as short circuit current) across H441 monolayers by approximately 50% compared with that of controls. Phenformin and AICAR significantly reduce amiloride-sensitive transepithelial Na+ transport compared with controls. Phenformin and AICAR suppress amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport across H441 cells via a pathway that includes activation of AMPK and inhibition of both apical Na+ entry through ENaC and basolateral Na+ extrusion via the Na+,K+-ATPase.
In vivo: Phenformin also increases levels of P-eIF2α and its target BiP/Grp78 in normal lung as well as in lung tumors of mice. Phenformin induces a significant increase in survival and therapeutic response in KLluc mice following long-term treatment. Phenformin-treated rats reveals a tendency towards a decrease in blood insulin level (radioimmunoassay).
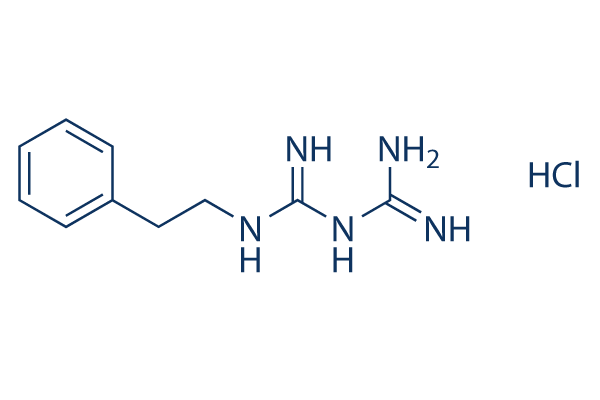
| Molecular Weight | 241.72 |
| Formula | C10H15N5.HCl |
| CAS Number | 834-28-6 |
| Solubility (25°C) | Water 12 mg/mL DMSO 9 mg/mL |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
| Related AMPK Products |
|---|
| Aldometanib
Aldometanib (LXY-05-029) is an orally active aldolase inhibitor. |
| SAMS
SAMS peptide is a specific substrate for the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). |
| Marein
Marein has the neuroprotective effect due to a reduction of damage to mitochondria function and activation of the AMPK signal pathway. |
| Malvidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride
Malvidin-3-O-arabinoside chloride ameliorates ethyl carbamate-induced oxidative damage by stimulating AMPK-mediated autophagy. |
| AMPK activator 12
AMPK activator 12 is a potent AMPK activator and GDF15 inducer. |
All AbMole products are for research use only, cannot be used for human consumption or veterinary use. We do not provide products or services to individuals. Please comply with the intended use and do not use AbMole products for any other purpose.


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2024 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
