N-acetyl-L-leucine (NALL) significantly improved motor and cognitive outcomes in the injured mice, led to the attenuation of cell death, and reduced the expression of neuroinflammatory markers after controlled cortical impact (CCI) induced experimental TBI in mice.
| Molecular Weight | 173.21 |
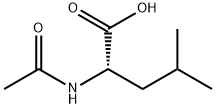
| Formula | C8H15NO3 |
| CAS Number | 1188-21-2 |
| Solubility (25°C) | DMSO ≥ 20 mg/mL |
| Storage |
Powder -20°C 3 years ; 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months ; -20°C 1 month |
| Species | Mouse | Rat | Rabbit | Guinea pig | Hamster | Dog |
| Weight (kg) | 0.02 | 0.15 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 10 |
| Body Surface Area (m2) | 0.007 | 0.025 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.5 |
| Km factor | 3 | 6 | 12 | 8 | 5 | 20 |
| Animal A (mg/kg) = Animal B (mg/kg) multiplied by | Animal B Km |
| Animal A Km |
For example, to modify the dose of Compound A used for a mouse (20 mg/kg) to a dose based on the BSA for a rat, multiply 20 mg/kg by the Km factor for a mouse and then divide by the Km factor for a rat. This calculation results in a rat equivalent dose for Compound A of 10 mg/kg.
| Related Metabolite/Endogenous Metabolite Products |
|---|
| 2,3-Dihydroxyisovaleric acid
2,3-Dihydroxyisovaleric acid is a natural metabolite of the branched-chain amino acid leucine. It acts by activating the mTOR signaling pathway to promote the synthesis of new muscle proteins and reduce the breakdown of existing proteins. |
| Ursocholic acid
Ursocholic acid is a bile acid found predominantly in bile of mammals, which can be transformed into deoxycholic acid by the intestinal microflora in mice. |
| 5β-Cholanic acid
5β-Cholanic acid can be used for 5β-Cholanic acid derivatives synthesis. |
| D-Thyroxine
D-Thyroxine is a thyroid hormone that can inhibit TSH secretion. D-Thyroxine can be used for the research of hypercholesterolemia. |
| Allolithocholic acid
Allolithocholic acid is a steroid acid could found in normal serum and feces. Allolithocholic acid facilitates excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. |


Products are for research use only. Not for human use. We do not sell to patients.
© Copyright 2010-2023 AbMole BioScience. All Rights Reserved.
